Diagrams are diagrams made up of lines drawn on paper to demonstrate some concept or theory. Their name comes from the Greek verb diagraphein, meaning to mark out by lines.
When reading a diagram, look out for labels and titles; these will give you more specific information, such as sales of ice cream in 2021.
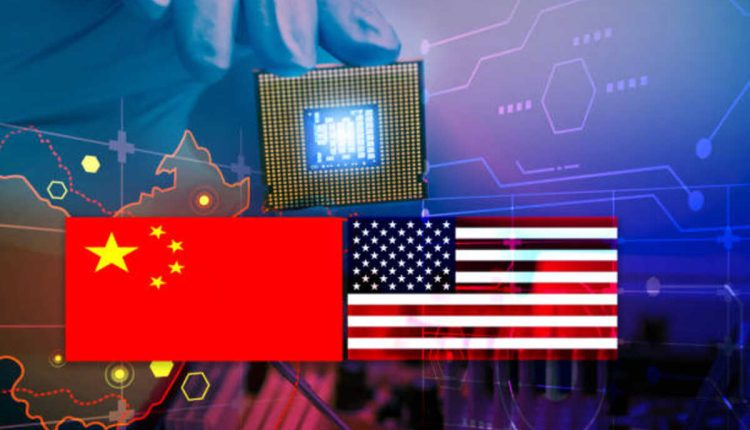
A. The United States Develops Interest in Chinese Markets
The United States increasingly seeks Chinese markets to support its economic growth and global security interests. But whether this strategy proves fruitful will depend on China’s shifting toward openness and permitting market forces to allocate resources efficiently. Presently, Beijing’s policy mix includes coercive practices, market restrictions, and other measures that create inefficiencies and vulnerabilities for firms located in both countries, leading to inefficiency that harms both economies despite attempts at supporting growth.
These policies have become more concerning because they contradict China’s stated reform goals. China’s senior leaders often stress the importance of allowing the market to play a decisive role, yet China imposes significant barriers to market access for American firms – such as forcing them to transfer technology over to Chinese partners – thus restricting market competition and favoring domestic firms over foreign.
Unravel: the policies enacted concurrently with China’s growing assertiveness on the world stage are worrying. China has increasingly attempted to form exclusive blocs like Five Eyes, Quad, and AUKUS in the Asia-Pacific region and force countries in this region into joining these entire blocs, as well as forcing regional nations into taking sides – practices which fuel tension and undermine peace.
The United States and China must develop more productive relations founded upon mutual respect and engagement in creating an open, fair, rules-based global economy. The US must stand up for its values as part of an international order it helped establish while ensuring China reflects them through policies.
Which phrase best completes the diagram?
B. The United States Develops Interest in Chinese Markets
The United States took an interest in Chinese markets because of its desire to remain an economic and political leader in the global economy. China’s growth is vital to international cooperation; however, its unfair trade practices threaten the system that enabled this growth – creating inefficiencies and vulnerabilities that threaten both parties involved.
Early United States governments developed an interest in Chinese markets due to their vast need for natural resources and goods with rapidly rising demand. Furthermore, the United States had long promoted democracy and human rights in Asia, and they feared China might become increasingly authoritarian and repressive of minority groups, making reform harder to implement and slowing economic development.
At the close of the nineteenth century, the United States was eager to gain access to Asia and Pacific natural resources to satisfy its rapidly increasing population and industry. To do this, they established several foreign policy objectives, including an Open Door policy to encourage free trade with nations within this region and procuring all resources required to sustain such growth.
Throughout this period, the United States also established several institutions to foster democracy and human rights around the globe. One such institution is the National Foundation for Infantile Paralysis – later renamed March of Dimes – founded in 1938 to raise money for research into birth defect prevention cures and provide financial aid for individuals and families living on limited incomes.
The United States was eager to capitalize on economic opportunities presented by emerging economies of the world, particularly China. To this end, trade agreements were made with various regional nations, while investment programs encouraged investment there. While America continues its pursuit of interests in Chinese markets, Beijing should address any unfair trade practices or improve governance standards before any future American investments occur there.
C. The United States Develops Interest in Chinese Markets
As China’s economic power increases, the United States becomes increasingly interested in Chinese markets. This development is vital for the global economy as it allows free trade with an emerging primary new market while remaining protected against China’s unfair policies and giving Americans experience working with Chinese companies and learning about its successes and failures.
Government intervention can be justified under certain circumstances, such as correcting market failures. However, government interventions can have disastrous economic repercussions when they go too far. China uses non-market tools more extensively and broadly than other major economies, creating domestically and externally inefficiencies and vulnerabilities for both countries.
Several events shaped U.S. foreign policy in the late 19th century. President Jackson annexed land west of the Mississippi River; America announced an Open Door policy towards Asia; and military alliances were created with European powers; these factors changed American influence around the globe.
The United States exerts international influence through economic and foreign policy actions. Through its alliance system and exclusive clubs like Five Eyes, Quad, and AUKUS, it has sought to increase global power and gain more significant influence internationally. However, this can potentially create division among regional countries and fuelling confrontation undermining peace.
The March of Dimes was built upon a grassroots approach to fundraising by millions of donors who gave small amounts each month, which in turn funded care and research of children with birth defects and their prevention and treatment. This grassroots fundraising model can also be applied by other groups using online donation platforms, making fundraising much more straightforward for everyone regardless of age, business venture, or cause they support.
D. The United States Develops Interest in Chinese Markets
United States investors have taken an increased interest in Chinese markets due to China’s recent economic transformation. Moving away from state ownership of companies towards market-based capitalism has helped bring this transformation, improving consumer quality goods and services while building consumer trust and creating jobs.
However, economic expansion in China has not come without difficulty. Not only must quality improve across goods and services, but rapid debt growth has alarmed analysts about financial stability; China’s government has adopted policies designed to mitigate risks while encouraging private sector development.
China has reduced taxes for corporations and investors to achieve this goal and introduced stricter regulations. They have also promoted social responsibility among businesses while ramping up agriculture and rural development support. Lastly, their investment strategies have shifted away from export-oriented industries toward high-tech sectors while investing in infrastructure and technology to promote economic development while improving security.
Beyond these improvements, China’s leadership has reiterated its intent to pursue “inclusive economic growth.” This means investing in its poorest regions while protecting large firms’ interests – an approach that should benefit global economics by creating jobs and supporting sustainable development.
The United States is strengthening its alliances in the Asia-Pacific region, piecing together small blocs such as Five Eyes and Quad, forcing regional countries into taking sides, and forcing division. Such moves create regional division, heighten conflict, and threaten peace. Supporting its allies to compete within global economic systems while upholding its principles will help preserve a prosperous international order – without which America would fall further behind its competitors.